The right pricing strategy can speed adoption, ensure profitability, enhance customer satisfaction, and position your brand effectively against competitors. However, determining the optimal price for your products or services requires more than just intuition. It demands an analysis of market conditions, customer perceptions, and competitor strategies.
Today, we'll explore various pricing analysis methods, explaining what they are and how to use them to optimize your pricing strategy.
What is Pricing Analysis?
Pricing analysis evaluates and sets prices for products or services to achieve specific business objectives. This involves gathering and analyzing data related to market trends, competitor pricing, and customer behavior to identify the optimal price point that maximizes profits and meets market demands.
A practical and effective pricing analysis combines qualitative and quantitative research methods to ensure that prices reflect the value perceived by customers while aligning with the company's financial goals.
Key Components of Pricing Analysis
Cost Analysis
Determining the total cost of production, including fixed and variable costs, to ensure that prices cover expenses and generate profit.
Market Analysis
Evaluating market trends and conditions to understand the broader economic environment and its impact on pricing.
Competitor Analysis
Assessing competitor prices and strategies to position your product competitively.
Customer Analysis
Understanding customer perceptions, preferences, and willingness to pay to ensure that prices resonate with the target audience.
Why is it Important to Conduct a Pricing Analysis?
Conducting a pricing analysis is crucial for several reasons:
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Profitability
Profitability
Accurate pricing ensures that a business covers costs and achieves a desirable profit margin. By understanding the actual cost of production and the value customers place on your product, you can set prices that maximize profitability.
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Competitiveness
Competitiveness
Analyzing competitor prices helps businesses stay competitive without engaging in destructive price wars. By knowing where your prices stand relative to competitors, you can adjust your strategy to attract more customers.
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Customer Satisfaction
Customer Satisfaction
Understanding customer perceptions and willingness to pay leads to pricing strategies that meet customer expectations and happier customers. People are more likely to remain loyal if they feel they receive good value for their money.
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Market Positioning
Market Positioning
Pricing can reinforce a brand's position in the market, whether as a premium offering or a budget-friendly option. Strategic pricing helps differentiate your product and establish your brand identity.
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Informed Decision-Making
Informed Decision-Making
Pricing analysis provides data-driven insights that help businesses make informed decisions about product launches, promotions, and discounts. This reduces the risk associated with pricing decisions and enhances overall business strategy.
Long-term Benefits of Pricing Analysis
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Sustainable Growth
Sustainable Growth
By continuously optimizing prices, businesses can achieve sustained growth and profitability.
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Improved Customer Relationships
Improved Customer Relationships
Transparent and fair pricing fosters trust and improves customer relationships.
_Size=sm)_Color=Success.png) Enhanced Brand Reputation
Enhanced Brand Reputation
A well-priced product that meets customer expectations enhances the brand's reputation and market standing.
Pricing Analysis Methods
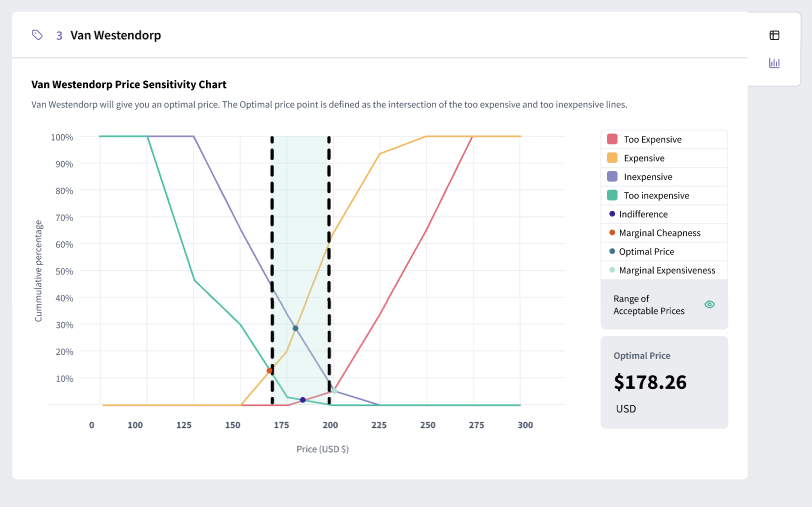
Price Sensitivity Testing (Van Westendorp)
The Van Westendorp Price Sensitivity Meter is a survey-based price analysis method that identifies the ideal price range for a product. This method balances affordability with perceived value to determine the acceptable price range and the optimal price point.
How to Use Price Sensitivity Testing
![]() Survey Design: Survey customers with four key questions about pricing perceptions:
Survey Design: Survey customers with four key questions about pricing perceptions:
- At what price do you consider the product to be too expensive?
- At what price do you consider the product to be too cheap?
- At what price do you consider the product to be a bargain?
- At what price do you consider the product to be expensive but still worth buying?
![]() Data Collection: Collect responses from a representative sample of your target market.
Data Collection: Collect responses from a representative sample of your target market.
![]() Data Analysis: Plot the responses to identify the intersections of the different price points. This analysis will reveal the optimal price range and acceptable price points.
Data Analysis: Plot the responses to identify the intersections of the different price points. This analysis will reveal the optimal price range and acceptable price points.
![]() Implementation: Set or adjust your pricing strategy using the identified price range.
Implementation: Set or adjust your pricing strategy using the identified price range.
Van Westendorp Example
A software company might use the Van Westendorp method to determine the price range for a new application by surveying potential users and analyzing their responses.
Pros and Cons of Price Sensitivity Testing
Pros: Provides clear insights into customer price perceptions and acceptable price ranges. Helps in setting prices that are aligned with customer expectations.
Cons: Results can be influenced by how the questions are framed and the respondents' understanding of the product. Requires careful survey design to ensure accuracy.
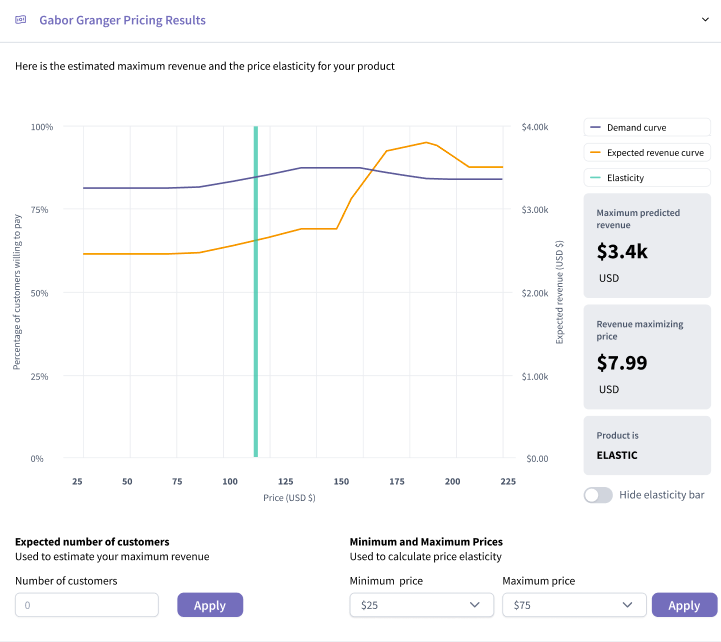
Gabor-Granger Technique
The Gabor-Granger price analysis technique measures the demand for a product at different price points to determine the optimal price that maximizes revenue. This method helps to determine how price changes affect customer purchase decisions.
How to Use a Gabor-Granger
![]() Survey Design: Present customers with different price points for a product and ask how likely they are to purchase at each price.
Survey Design: Present customers with different price points for a product and ask how likely they are to purchase at each price.
![]() Data Collection: Gather responses from a large, representative sample to ensure statistical validity.
Data Collection: Gather responses from a large, representative sample to ensure statistical validity.
![]() Data Analysis: Analyze the responses to create a demand curve that shows the relationship between price and purchase likelihood.
Data Analysis: Analyze the responses to create a demand curve that shows the relationship between price and purchase likelihood.
![]() Implementation: Identify the price point that maximizes revenue based on the demand curve and adjust your pricing strategy accordingly.
Implementation: Identify the price point that maximizes revenue based on the demand curve and adjust your pricing strategy accordingly.
Gabor-Granger Example
An electronics retailer might use the Gabor-Granger technique to find the optimal price for a new gadget by surveying potential buyers and analyzing their willingness to purchase at various price points.
Pros and Cons of Gabor-Granger Price Analysis
Pros: Provides detailed insights into price elasticity and demand at various price points. Helps in setting prices that maximize revenue.
Cons: Requires a large sample size to ensure accurate results and may not account for competitive dynamics.
Conjoint Analysis
Conjoint analysis is a statistical method that evaluates how customers value different features and attributes of a product, including price. This method helps understand the trade-offs customers are willing to make between different product features and price.
How to Use Conjoint for Pricing Analysis
![]() Survey Design: Design a survey that presents respondents with different product configurations, each with varying features and prices.
Survey Design: Design a survey that presents respondents with different product configurations, each with varying features and prices.
![]() Data Collection: Ask respondents to choose their preferred configuration from a set of options.
Data Collection: Ask respondents to choose their preferred configuration from a set of options.
![]() Data Analysis: Use statistical analysis to determine the relative importance of each feature and the optimal price point.
Data Analysis: Use statistical analysis to determine the relative importance of each feature and the optimal price point.
![]() Implementation: Apply the insights to set prices and design products that meet customer preferences.
Implementation: Apply the insights to set prices and design products that meet customer preferences.
Conjoint Price Analysis Example
A car manufacturer might use conjoint analysis to understand how customers trade-off between features like engine size, fuel efficiency, and price, helping to set optimal prices for different configurations.
The Pros and Cons of Using Conjoint Analysis for Pricing
Pros: Provides comprehensive insights into customer preferences and the trade-offs they are willing to make. Helps in designing products that align with customer expectations.
Cons: It can be complex to design and analyze and requires advanced statistical expertise.
Concept Testing
Concept testing involves presenting potential customers with a new product concept, including its features and proposed price, to gauge their reactions and willingness to purchase. This method helps validate new product ideas and pricing before launch.
How to Use Concept Testing in Pricing Analysis
![]() Concept Development: Develop a detailed concept description, including the product's features, benefits, and proposed price.
Concept Development: Develop a detailed concept description, including the product's features, benefits, and proposed price.
![]() Survey Design: Survey potential customers to gather feedback on the concept and their likelihood of purchasing at the proposed price.
Survey Design: Survey potential customers to gather feedback on the concept and their likelihood of purchasing at the proposed price.
![]() Data Collection: Collect and analyze the feedback to refine the product concept and pricing strategy.
Data Collection: Collect and analyze the feedback to refine the product concept and pricing strategy.
![]() Implementation: Use the insights to adjust the product and its pricing before the market launch.
Implementation: Use the insights to adjust the product and its pricing before the market launch.
Concept Testing Example
A food and beverage company might use concept testing to evaluate a new snack product's appeal and determine the optimal price point based on customer feedback.
The Pros and Cons of Using Concept Testing in Price Analysis
Pros: Provides direct feedback from potential customers and can validate product concepts before launch. Helps in fine-tuning product features and pricing.
Cons: Results can be influenced by how well the concept is communicated and the survey design. Requires thorough analysis to draw actionable insights.
Numeric Price Entry
Numeric price entry involves asking customers to input the exact amount they are willing to pay for a product, providing direct insights into their price sensitivity. This method captures precise data on customer willingness to pay.
How to Use Numeric Price Entry
![]() Survey Design: Design a survey that asks customers to specify the price they would be willing to pay for a product or service.
Survey Design: Design a survey that asks customers to specify the price they would be willing to pay for a product or service.
![]() Data Collection: Gather responses from a representative sample of your target market.
Data Collection: Gather responses from a representative sample of your target market.
![]() Data Analysis: Analyze the responses to identify common price points and the range of acceptable prices.
Data Analysis: Analyze the responses to identify common price points and the range of acceptable prices.
![]() Implementation: Use this data to set or adjust your pricing strategy to align with customer expectations.
Implementation: Use this data to set or adjust your pricing strategy to align with customer expectations.
Example of a Numeric Price Entry
An online retailer might use numeric price entry to understand how much customers are willing to pay for a new subscription service, helping to set a competitive and profitable price.
Pros and Cons of Using Numeric Price Entry
Pros: Provides precise data on customer willingness to pay and can reveal insights into price sensitivity. Helps in setting prices that match customer expectations.
Cons: Responses can vary widely, and some customers may provide unrealistic price points. It requires careful analysis to derive meaningful insights.
Conducting a Pricing Analysis with SightX
No matter the method you choose, SightX's AI-powered tools make pricing analysis easier, faster, and more accurate than ever before.
By infusing the power of generative AI with advanced price analysis tools, you can:
![]() Create fully customized price analysis studies and experiments with a prompt, like: "I need to find the ideal price point for my product. Create a Gabor-granger study."
Create fully customized price analysis studies and experiments with a prompt, like: "I need to find the ideal price point for my product. Create a Gabor-granger study." ![]() Collect data from your target audience.
Collect data from your target audience. ![]() Receive fully analyzed and summarized results in seconds, revealing key brand insights and personalized recommendations.
Receive fully analyzed and summarized results in seconds, revealing key brand insights and personalized recommendations.
Whether it's understanding the price sensitivity in your market, exploring demand fluctuations, or finding the ideal price point, SightX offers a comprehensive suite of pricing research features designed to streamline the process and deliver results fast.
Let us show you how simple it can be to collect powerful brand insights.
